lv dysfunction medical abbreviation | what is lv function lv dysfunction medical abbreviation Left ventricular failure occurs when there is dysfunction of the left ventricle causing insufficient delivery of blood to vital body organs. Explore our list of 18th Century Historical Fiction - General & Miscellaneous Books at Barnes & Noble®. Get your order fast and stress free with free curbside pickup.
0 · what is severe lv dysfunction
1 · what is lv function
2 · treatment for lv hypertrophy
3 · severely decreased lv systolic function
4 · severe lv impairment
5 · lv medical abbreviation meaning
6 · lv medical abbreviation cardiology
7 · lv ejection fraction chart
$4,500.00
vintage rolex styles
what is severe lv dysfunction
Left ventricular dysfunction is the medical name for a weak heart pump. It's a condition that impacts about 9% of people over the age of 60, which is around 7 million Americans. In this Mayo Clinic Minute, Dr. Paul Friedman , a Mayo Clinic cardiologist , .Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. Th. Left ventricular dysfunction (LVD) with subsequent congestive heart failure (CHF) .
what is lv function
Left-sided heart failure affects the heart’s ability to pump blood. It includes .
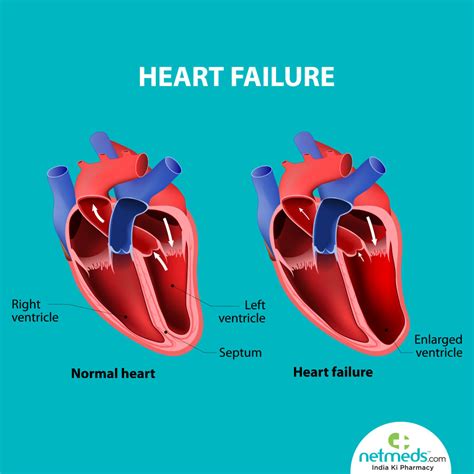
Left ventricular failure occurs when there is dysfunction of the left ventricle causing insufficient delivery of blood to vital body organs. Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart chamber from filling properly with blood.
Systolic heart failure, also called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, occurs when your . There are two types of left-sided heart failure: Systolic failure: The left ventricle loses its ability to contract normally. The heart can't pump with enough force to push enough blood into circulation. This is also known as .
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) means your left heart .Known Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction. If no established diagnosis of heart failure, please . Left ventricular dysfunction is the medical name for a weak heart pump. It's a condition that impacts about 9% of people over the age of 60, which is around 7 million Americans. In this Mayo Clinic Minute, Dr. Paul Friedman , a Mayo Clinic cardiologist , explains what the condition is and how it can be diagnosed and treated. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending the blood out into your circulation.
Left ventricular dysfunction (LVD) with subsequent congestive heart failure (CHF) constitutes the final common pathway for a host of cardiac disorders. Coronary artery narrowing or ischaemic heart disease is the dominant cause of heart failure and is often associated with acute or prior myocardial infarction. Left-sided heart failure affects the heart’s ability to pump blood. It includes diastolic dysfunction and systolic heart failure. Left ventricular failure occurs when there is dysfunction of the left ventricle causing insufficient delivery of blood to vital body organs. Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart chamber from filling properly with blood.
Systolic heart failure, also called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, occurs when your left ventricle can’t pump blood efficiently. It’s a serious condition and can cause damage to other organs. Treatment addresses any underlying causes, such as coronary artery disease or hypertension, along with lifestyle changes. There are two types of left-sided heart failure: Systolic failure: The left ventricle loses its ability to contract normally. The heart can't pump with enough force to push enough blood into circulation. This is also known as heart failure with reduced ejection, or HFrEF. Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) means your left heart ventricle has weakened and less blood is being pumped into your body. HFrEF requires ongoing treatment to.Known Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction. If no established diagnosis of heart failure, please see referral for suspected diagnosis of heart failure page. For patients with an established diagnosis of heart failure: Classify severity according to NYHA score.
Left ventricular dysfunction is the medical name for a weak heart pump. It's a condition that impacts about 9% of people over the age of 60, which is around 7 million Americans. In this Mayo Clinic Minute, Dr. Paul Friedman , a Mayo Clinic cardiologist , explains what the condition is and how it can be diagnosed and treated.
Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending the blood out into your circulation.Left ventricular dysfunction (LVD) with subsequent congestive heart failure (CHF) constitutes the final common pathway for a host of cardiac disorders. Coronary artery narrowing or ischaemic heart disease is the dominant cause of heart failure and is often associated with acute or prior myocardial infarction.
Left-sided heart failure affects the heart’s ability to pump blood. It includes diastolic dysfunction and systolic heart failure. Left ventricular failure occurs when there is dysfunction of the left ventricle causing insufficient delivery of blood to vital body organs. Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart chamber from filling properly with blood.Systolic heart failure, also called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, occurs when your left ventricle can’t pump blood efficiently. It’s a serious condition and can cause damage to other organs. Treatment addresses any underlying causes, such as coronary artery disease or hypertension, along with lifestyle changes.
There are two types of left-sided heart failure: Systolic failure: The left ventricle loses its ability to contract normally. The heart can't pump with enough force to push enough blood into circulation. This is also known as heart failure with reduced ejection, or HFrEF. Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) means your left heart ventricle has weakened and less blood is being pumped into your body. HFrEF requires ongoing treatment to.
treatment for lv hypertrophy
severely decreased lv systolic function
rolex op white 36
vintage rolex pilot watch
Produced Tanks starting in 1919. Headed by Louis Cartier from 1903-1942 , Pierre Cartier 1942-1947, non-family heads (1947-1966) (sold to holding company in 1966) Movements from Jaeger + LeCoultre (later JLC proper), Piguet, Piaget, Journe, and more.
lv dysfunction medical abbreviation|what is lv function